AI Assistant for Mental Health: Your Guide to Accessible, Everyday Support

AI is everywhere, including mental healthcare. Maybe that’s why you’ve decided to see how an AI assistant for mental health could help you feel better. But the moment you start looking… Well, there are so many AI assistants out there that choosing the right one feels like trying to pick your favorite song from a playlist of hundreds.
That’s why we put this guide together to help you understand the different types of AI assistants for mental health support, show you which AI mental-health apps are worth exploring, and teach you how to use an AI companion with confidence and peace of mind.
Key Learnings
- AI assistants make mental health support easier to access, more private, and available 24/7.
- The market includes three main types of tools: emotional companions, therapeutic skill coaches, and self-reflection assistants.
- Studies show AI can reduce symptoms and support daily well-being. Still, it works best when used responsibly along with professional therapy.
Why People Turn to AI for Mental Health Support
According to recent statistics, 1 in 3 people in the UK have turned to chatbots for support (with 64% of those users aged 25–34). Meanwhile, in the US, a study shows that approximately 1 in 8 people aged 12–21 have engaged in the same behavior, along with more than 1 in 4 adults overall.
1. Affordable and Accessible
Long waitlists and costs are the biggest hurdles to good-quality mental health services. In fact, 41% of those who used an AI emotional health assistant claim that they did so because of the ease of access: unlike traditional therapy support, AI in the mental health field is low-cost and comes with no waitlists.
2. Private & Anonymous
Artificial intelligence doesn’t judge. Unlike one’s relatives, who always have unsolicited opinions (24% of AI users have turned to AI because they felt uncomfortable sharing their worries with friends or family), anonymity in AI interactions creates that safe space that encourages people to express themselves without fear of judgment or stigma.
3. 24/7 Emotional Availability
Unlike human therapists, AI models are there for you 24/7: during late-night spirals, early-morning anxiety, or unexpected stressful situations. Sure, AI systems aren’t replacements for sessions with qualified therapists. However, an AI emotional health assistant is a great tool if you:
- Need immediate, non-judgmental venting.
- Get mental health support in low-stress daily situations.
- Want to learn some structured self-help techniques (like CBT/DBT).
They’re also a great option if you’re looking for additional support between your therapy sessions to practice coping skills and maintain progress.
Types of AI Assistants for Mental Health on the Market
Here are 3 main types of AI assistants for mental healthcare that modern AI-powered apps might include.
Emotional Support and Companion Bots
These AI assistants focus on connection, empathy, companionship, and emotional presence. They're all about being there for you when you need someone to talk to.
- Warm, emotionally validating conversations.
- Supportive check-ins for loneliness, anxiety, or everyday stress.
- A sense of companionship that grows through ongoing chats.
- Safe space for venting without stigma or expectations.
- Gentle recommendations like meditation or breathing exercises during challenging moments.
Examples of Emotional Support and Companion Bots
| App | Core Purpose / Focus | AI Assistant Feature |
| Livie (Liven) | Emotional presence, reflection, and supportive dialogue | Warm, compassionate AI; perfect for daily check-ins, grounding, and feeling understood. |
| Replika | Long-term companionship & emotional connection | Open-ended chat; remembers user stories; acts as an “AI friend.” |
| Ebb (Headspace) | Mindfulness & reflection support | Chat-based check-ins + personalized meditation. |
Therapeutic Skill Coaches (CBT/DBT Approach)
These AI assistants focus on evidence-based techniques used in therapeutic approaches like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT), or Acceptance & Commitment Therapy (ACT).
❗️ Please keep in mind that these apps aren’t licensed therapists.
They often offer:
- CBT-based exercises to challenge unhelpful thinking patterns.
- DBT techniques for grounding, emotional regulation, and distress tolerance.
- Psychoeducation modules that teach how thoughts, feelings, and behaviors connect.
- Mindfulness and calming exercises are integrated into the chat.
- Early intervention support when users notice worsening symptoms.
Examples of Therapeutic Skill Coaches (CBT/DBT Approach)
| App | Core Purpose / Focus | AI Assistant Feature |
| Woebot | CBT-based emotional skill-building | Structured daily CBT lessons and check-ins |
| Wisa | CBT/DBT, mindfulness, solution-focused therapy | Guided exercises embedded in chat |
| Youper | CBT, ACT, DBT for anxiety & depression | Symptom screening + adaptive interventions |
AI Assistants for Reflection and Self-Exploration
These AI tools focus on introspection, emotional awareness, and personal growth.
They often offer:
- Guided emotional reflection to help you put tangled feelings into words;
- Structured journaling prompts to uncover hidden thoughts, stress sources, or patterns you didn’t notice;
- Personalized reflection exercises: grounding practices, value-identification exercises, or self-kindness prompts;
- A private, judgment-free space — you can safely explore your inner world without judgment or pressure.
Examples of AI Assistants for Reflection and Self-Exploration
| App | Core Purpose / Focus | AI Assistant Feature |
| Ash AI | Guided journaling and emotional insight | Conversational prompts that help users verbalize inner experiences |
| Mindsera | AI-augmented journaling and mindset development | Chat-based reflection with structured introspection exercises |
| Pi (Inflection AI) | Emotional reflection & self-understanding | Empathetic conversational AI supports everyday emotional check-ins |
Top AI Assistants for Mental Health, Compared
| Type | What they do | What to keep in mind | App examples |
| Reflection / Self-Exploration | Prompt you to reflect, help track mood, notice emotional patterns, and journal thoughts. | Less “therapy”, more self-awareness | Ash AI, Mindsera. Pi (Inflection AI) |
| Therapeutic Skill Coaches (CBT/DBT) | Offer CBT-based exercises, structured support for anxiety, and teach coping skills. | Works well for mild to moderate symptoms; limited for complex mental health crises | Woebot, Wisa, Youper |
| Emotional Support / Companion Bots | Offer conversation, companionship, and nonjudgmental listening. | Less structured support | Liven, Replika, Headspace |
How to Use an AI Assistant for Mental Health
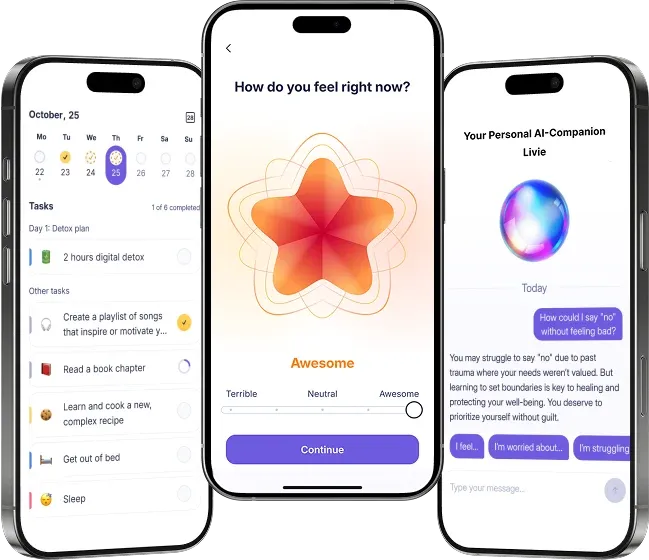
Here is how to get the most from your communication with artificial intelligence assistants for mental healthcare in daily life. We’ll use Livie as an example.
Start with Gentle Reflection
There’s no need to come in “prepared” or know what to say. You can start with:
- “I feel off today, but I’m not sure why.”
- “Something’s been bothering me.”
- “I woke up anxious.”
Livie will ask you gentle questions to help you see what’s at the core of your emotional state and what the relief might be.
Practice Coping Strategies
Livie can offer and help you practice the following calming strategies during stressful situations:
- Grounding
- Reframing your thoughts
- Naming emotions
- Breathing techniques
These aren’t clinical interventions; however, they’re good everyday emotional health tools that help regulate stress and deal with difficult moments.
Additionally, Livie will guide you on how to utilize the Liven app for even greater benefits in specific cases. For instance, you’re telling Livie you’ve been feeling highly anxious recently. In response, Livie can offer to use the Mood Tracker (and explain how it works) and explore the anxiety management course available in the app.
Track Progress Consistently
Regular check-ins help you monitor your emotional health and notice when something needs extra attention.
Livie tracks and summarizes chats for you. This means you can see when and how you felt, what the trigger was, and the coping techniques that Livie offered.
Using AI Assistants Responsibly: Recommendations
✅ Use them as complementary support, not a replacement for professional therapy. AI tools can aid in mood tracking, self-reflection, and the development of coping skills, such as reframing and breathing techniques. However, they don’t substitute real-life therapists, especially for severe mental health conditions.
✅ Check privacy, data security, and what the app promises. Some apps collect a lot of data. So, make sure to trust the app before sharing personal information — look for genuine user reviews online and review the app’s data policies.
✅ Use human support and offline strategies too. Social interaction, physical activity, hobbies, and professional support: all these elements matter because they form a genuine support system in real life.
Can AI Really Help Our Mental Health? What Research Shows
Across reviews, clinical trials, and ethical studies, several themes consistently emerge: AI aids in access and symptom reduction, but safety, privacy, and over-reliance on AI remain significant concerns.
The research also indicates that AI can analyze mental health signals in surprising ways. For instance, AI tools can analyze speech patterns or videos to pick up signs of depression, PTSD, ADHD, or autism.
One study even created an AI that diagnosed mental disorders with 89% accuracy using just 28 questions, which is a lot faster than traditional methods. But when scientists compared Woebot — one of the biggest mental-health chatbots — to simpler tools like journaling apps, Woebot didn’t outperform them. This means chatbots aren’t automatically better just because they use AI.
Another issue is that people sometimes expect too much from chatbots. One study showed that users often believe that an average artificial intelligence system in mental healthcare is basically an “AI therapist,” even though these artificial intelligence models don’t offer effective online therapy and can’t handle crises.
Meanwhile, a review of 15 studies found that chatbots can help reduce symptoms of depression, anxiety, and stress. But they also noticed that people often stop using them over time, which limits their long-term impact. A massive meta-analysis confirmed this: after screening 7,834 studies, researchers found that AI noticeably reduces depression and distress.
Others examined 97 research papers and found that most chatbots use simple text messages, primarily based on CBT, and mainly target depression. However, many still don’t support cultural differences or high-risk situations well enough.
But even when AI in mental healthcare is helpful, researchers say its design matters. Some papers focus on the ethics of digital mental-health chatbots, explaining that bias, unfair treatment, data privacy issues, and unsafe advice can appear if systems aren’t built with care. When scientists examined the artificial intelligence tools used in online CBT programs, they found that AI can help therapists identify which clients require additional support, provided that humans remain in control.
Final Thoughts
AI is a valuable tool that makes mental health support more accessible, private, and available on your schedule, especially when combined with real-life therapy sessions and grounding habits like journaling, meditation, and movement.
If you feel inspired to go further, you can continue your self-discovery journey with Liven: start with the Liven app (Google Play or App Store, explore meaningful articles on the Liven blog, and learn more about your current state with Liven’s free wellness tests.
References
- Casu, M., et al. (2024). AI chatbots for mental health: A scoping review of effectiveness, feasibility, and applications. Applied Sciences, 14(5889). https://doi.org/10.3390/app14135889
- Jafar, A., Shabnam, S., & Khan, A. (2025). Artificial intelligence in mental healthcare: Opportunities, risks, and regulations. In AI in mental health: Innovations, challenges, and collaborative pathways (p. 40). https://doi.org/10.4018/979-8-3373-5072-1.ch014
- Kuhail, M. A., et al. (2025). A systematic review on mental health chatbots: Trends, design principles, evaluation methods, and future research agenda. https://doi.org/10.1155/hbe2/9942295
- Li, H., et al. (2023). Systematic review and meta-analysis of AI-based conversational agents for promoting mental health and well-being. npj Digital Medicine, 6, 236. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41746-023-00979-5
- Thieme, A., et al. (2023). ACM Transactions on Computer-Human Interaction, 30(2), Article 27. https://doi.org/10.1145/3564752
- Tutun, S., et al. (2023). An AI-based decision support system for predicting mental health disorders. Information Systems Frontiers, 25, 1261–1276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-022-10282-5
- [Frontiers Digital Health]. (2023). Key challenges for AI application in digital mental health. Frontiers in Digital Health, 5. https://doi.org/10.3389/fdgth.2023.1278186
- [AI in Mental Health Diagnosis and Treatment]. (2023). Pioneering approaches in health and wellness, 2(3).
FAQ: AI Assistant for Mental Health
Can an artificial intelligence assistant for mental health help with mental health conditions?
How do AI tools improve mental healthcare access?
Are AI-driven solutions safe for patient data?
Can AI therapy replace human therapists?
How do AI-powered assistants support Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) or Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)?
Can AI in mental health track healing progress effectively?
Do AI assistants provide support during a mental health crisis?
How does a conversational interface help in mental health apps?